Abstract
Introduction: The 2-part phase 3 CASSIOPEIA study (NCT02541383) investigated the combination of DARA with VTd (D-VTd) in transplant-eligible NDMM pts. D-VTd induction/consolidation (ind/cons) led to increased rates of MRD negativity and prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) compared with VTd (Moreau P, et al. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):29-38). In Part 2, DARA as post-autologous stem cell therapy (ASCT) maintenance significantly improved PFS in pts who received VTd ind/cons. Most common (≥2.5%) grade 3/4 adverse events included pneumonia (DARA: 2.5%; observation [OBS]: 1.4%), lymphopenia (3.6%; 1.8%), and hypertension (3.0%; 1.6%; Moreau P, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(no. 15_suppl):8004). Here, we present results from a detailed analysis of MRD negativity.
Methods: Eligible pts were 18-65 years of age, had NDMM and were ASCT eligible. Pts were randomized 1:1 to 4 (28-day) cycles of pre-ASCT induction and 2 (28-day) cycles of post-ASCT consolidation with D-VTd or VTd (bortezomib, 1.3 mg/m 2 SC on Days 1, 4, 8, 11; thalidomide, 100 mg PO daily; dexamethasone, 20-40 mg IV/PO; ± DARA, 16 mg/kg IV weekly (QW) in Cycles 1-2, Q2W in Cycles 3-6). Pts who completed consolidation and achieved partial response or better were re-randomized 1:1 to maintenance DARA at reduced intensity (DARA, 16 mg/kg Q8W) for a maximum of 2 years, or OBS. Samples were collected for MRD analysis at predefined timepoints from all pts regardless of response to ind/cons and in pts with very good partial response or better during maintenance. The primary MRD assessment methodology was multiparametric flow cytometry during ind/cons and next-generation sequencing during maintenance, each at the 10 -5 threshold. MRD negativity is reported here for pts who achieved complete response or better.
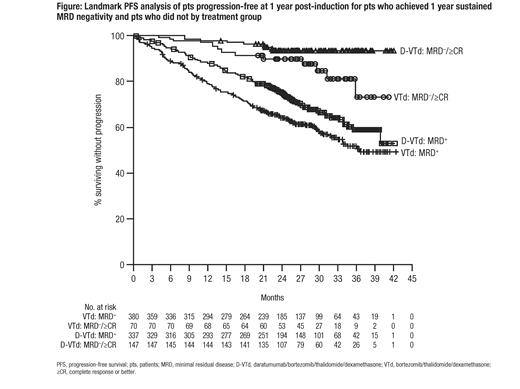
Results: 1,085 pts were randomized to ind/cons (D-VTd, n=543 or VTd, n=542) and 886 pts were re-randomized for post-ASCT maintenance (DARA, n=442 or OBS, n=444). The rate of MRD negativity was higher with D-VTd than with VTd following induction (9.2% vs 5.4%; odds ratio [OR], 1.79; P=0.0150) and consolidation (33.7% vs 19.9%; OR, 2.06; P<0.0001). Sustained MRD-negativity was higher in the D-VTd group compared to VTd at 1-year (50.1% vs 30.1%; OR, 2.37; P<0.0001) and at 2 years (35.5% vs 18.8%; OR, 2.41; P<0.0001). Among pts who were at risk of progression 1 or 2 years after induction, those who achieved, respectively, 1- or 2-years sustained MRD negativity from post-induction, showed improved PFS over pts who did not, regardless of treatment (1yr sustained: HR, 0.20; P<0.0001; 2yr sustained: HR, 0.08; P<0.0001). D-VTd pts at risk who achieved 1- or 2-years sustained MRD negativity from post-induction showed improved PFS over D-VTd pts who did not (1yr sustained: HR, 0.20; P<0.0001; 2yr sustained: HR, 0.04; P<0.0001). VTd pts at risk who achieved 1- or 2-years sustained MRD negativity from post-induction showed improved PFS over VTd pts who did not (1yr sustained: HR, 0.40; P=0.0030; 2yr sustained: HR, 0.22; P<0.0046; Figure).
During maintenance, the rate of MRD negativity significantly favored DARA over OBS (58.6% vs 47.1%; OR, 1.80; P=0.0001). In pts who received D-VTd ind/cons, the MRD-negativity rates with DARA and OBS were 64.2% and 57.6% respectively (OR, 1.43; P=0.1037). In contrast, pts who had received VTd ind/cons showed significantly higher MRD-negativity rates during DARA maintenance vs OBS (52.6% vs 35.8%; OR, 2.26; P=0.0002). The rates of sustained MRD negativity in the D-VTd group were not significantly different with DARA vs OBS (1yr sustained: 48.5% vs 41.0%; OR, 1.41; P=0.0885; 2yr sustained: 28.8% vs 21.8%; OR, 1.47; P=0.0789). In the VTd group, the 1-year sustained MRD-negativity rate was significantly higher with DARA vs OBS (35.7% vs 21.4%; OR, 2.22; P=0.0006) but no difference was observed in the 2-year sustained MRD rate (11.3% vs 13.0%; OR, 0.83; P=0.5481).
Conclusion: In CASSIOPEIA, the highest and most durable rates of MRD negativity were achieved after D-VTd ind/ASCT/cons and DARA maintenance. Reduced intensity (Q8W) DARA maintenance did not significantly improve MRD negativity compared to OBS in patients treated with D-VTd. In patients treated with VTd, DARA maintenance did improve MRD negativity, but this effect was not long lasting. Longer follow-up is required to assess the potential long-term benefits of sustained MRD negativity for DARA vs OBS after D-VTd.
Sonneveld: Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; SkylineDx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Moreau: Amgen: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene BMS: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Oncopeptides: Honoraria. van der Velden: Janssen: Other: Service Level Agreement; BD Biosciences: Other: Service Level Agreement; Navigate: Other: Service Level Agreement; Agilent: Research Funding; EuroFlow: Other: Service Level Agreement, Patents & Royalties: for network, not personally. Hulin: abbvie: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria. Arnulf: Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celene/BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mohty: Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria. Karlin: Janssen: Honoraria, Other: member of advisory board, travel support; Abbvie: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: travel support and advisory board ; Sanofi: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: member of advisory board; Celgene-BMS: Honoraria, Other: member of advisory board; GSK: Honoraria, Other: member of advisory board; oncopeptide: Honoraria. Macro: Sanofi: Honoraria; GSK: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Travel accomodation, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Travel accomodation, Research Funding; Celgen/BMS: Honoraria. Perrot: GSK: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Levin: Roche, Janssen, Abbvie: Other: Travel Expenses, Ad-Board. Delforge: Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding. Zweegman: Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Van De Donk: BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Novartis /bayer/servier: Consultancy. Krevvata: Janssen: Current Employment. Rigat: Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Yang: Janssen: Current Employment. Vanquickelberghe: Janssen: Current Employment. de Boer: Janssen: Current Employment. Kampfenkel: Janssen: Current Employment. Vermeulen: Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Broyl: Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Bristol-Meyer Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria.
The specific regimen combination is not yet approved in the maintenance setting.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal